What Can You Do With A Master of Engineering (MEng) Degree?
If your aim is to become a chartered engineer, a Master in Engineering (MEng) will help you advance your career to the next level. However, the qualification is available in different forms in various countries. But ultimately, they all serve as a pre-requisite for becoming a chartered engineer.
For more information about which career paths other Master’s degrees can lead you towards, click the image below.
Below are some simple overviews of the MEng degree and which career path it can lead you towards.
What is an MEng?
MEng is a specialised Master’s degree in Engineering. Comparatively, those who study it intend to become a professional or chartered engineer or in a related field. As a result, it’s accredited by official bodies responsible for overseeing these professions.
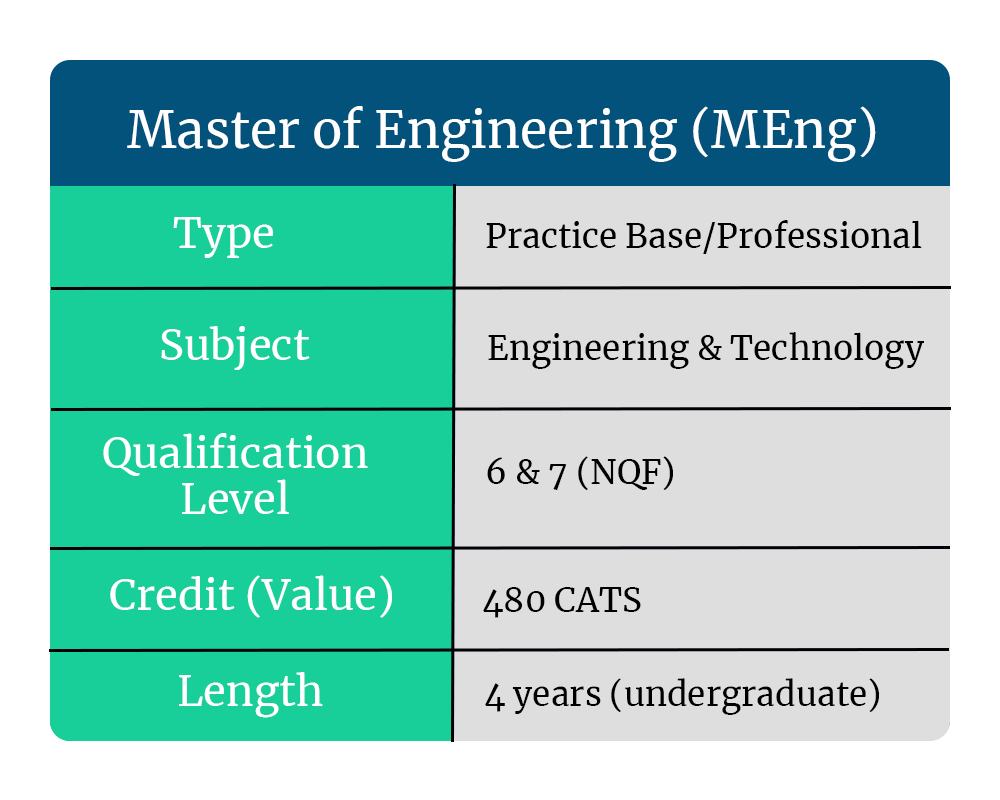
MEng is mostly used within Anglophone countries. However, in Europe, a Diploma in Engineering (or a similar version) is used instead. This can be used to refer to the modern Masters as well as an older version which may pre-date the Bologna Process. Whereas in Asia, most universities use the term Master of Technology (MTech) although there are variations. This Master’s is awarded to students in Engineering or Technology.
Entry requirements
In fact, the requirements for an MEng depend on the programme chosen as there are only two common versions; an undergraduate (integrated) or postgraduate qualification.
Integrated MEng
Will follow an undergraduate application process and runs for four years. This can be done in the UK and in some European countries.
Postgraduate MEng
Will require an appropriate bachelor’s degree, although some universities may only ask for a Bachelor in Engineering (BEng) with grades 2.1 or higher. The MEng can last up to 2 years.
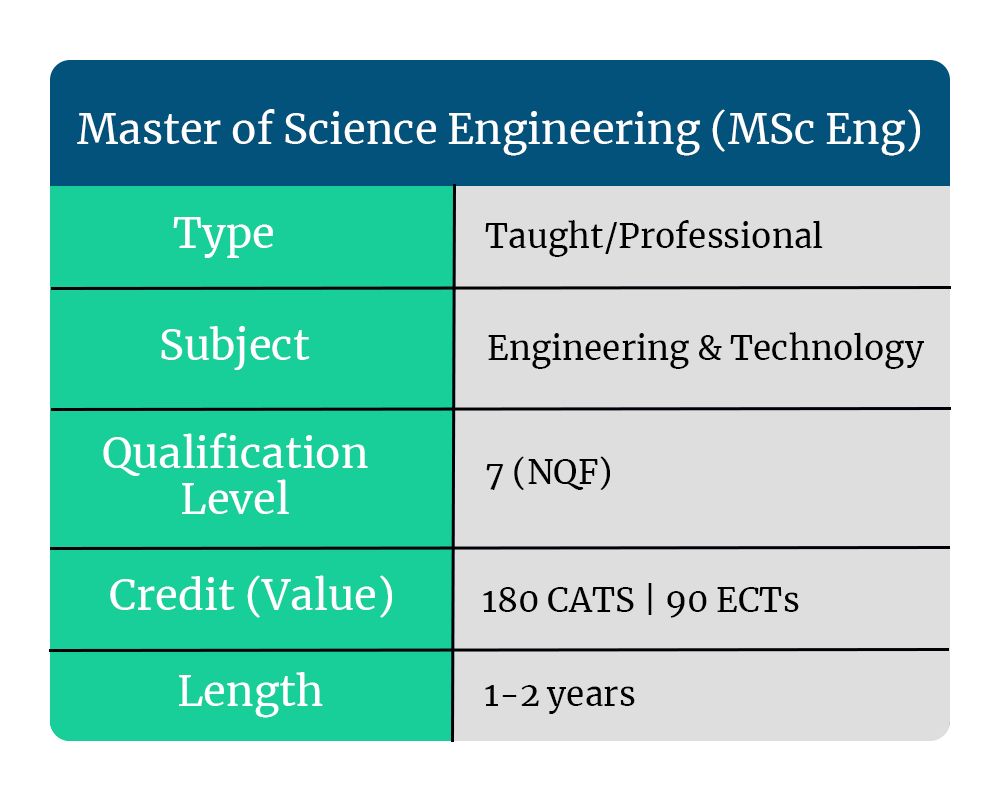
What is an MSc (Eng)?
In the UK, MEng is typically an integrated qualification in which students will study for 4 years as a Bachelor’s and a Master’s in one. However, some universities offer a standalone Master’s degree in Engineering called Master of Science in Engineering (MSc Eng). Therefore, this degree requires you to have a relevant Bachelor’s degree.
Which countries award an MEng and MSc (Eng)?
Most countries have a recognised Master in Engineering qualification as part of professional accreditation.
UK
The UK offers both an MEng and an MSc (Eng). Both qualifications can prepare you to qualify as an engineer in the UK provided that your Master’s is recognised by the UK Engineering Council. In spite of this, you may need to complete further training and/or professional qualifications to gain a Chartered Engineer status (CEng).
Europe
Unlike the UK, a Master’s in Engineering in Europe is in line with the Bologna Process. Previously, the qualification in Engineering was similar to the UK-integrated MEng although often labelled as Diploma rather than a Master’s. Diplomas are still available but many are moving to the conventional degree which can last up to 2 years.
USA
In the USA, MEng is a professional graduate program offered by specialised schools. Some offer an MEng or MSc (Eng) coupled with each other as part of a broader program in Engineering and Technology. Therefore, MEng is an end-degree that paves the way to becoming a recognised professional accredited engineer.

Which subjects award an MEng and MSc (Eng)?
To point out the obvious, the subjects which award an MEng or MSc (Eng) specialise in engineering. In modern universities, engineering is a very broad field. Therefore, you will be able to select your chosen degree in a broad or linear range of specialisms including;
- Aeronautical Engineering
- Automotive Engineering
- Chemical Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Electronic Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- System Engineering
How long is it and how many credits is it worth?
In the UK, MEng is worth 480 credits. 360 credits are split for the first 3 years of the equivalent Bachelor’s degree whereas the final 120 credits are awarded during your last year. However, an MSc (Eng) is only worth 180 credits.
Which career path can it steer you towards?
In either case, as these are specific specialised degrees, your career prospects are tied to engineering. As such, you can progress into engineering roles such as;
- Aerospace Engineer
- Automotive Engineer
- Civil Engineer
- Maintenance Engineer
- Mechanical Engineer
- Mining Engineer
- Nuclear Engineer
- Production Engineer
Whichever role you decide to progress to with the degree, remember the training and materials you have learned during your course. If you are unsure if you want to progress into an engineering Master’s, click the image below to find where other Master’s can lead you.



